Significant Improvement in Lung Function with an Evening & Morning Dose1
TUDORZA® PRESSAIR® (aclidinium bromide inhalation powder) is indicated for the maintenance treatment of patients with COPD.
TUDORZA PRESSAIR is not indicated for the initial treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm (i.e. rescue therapy).1
-
REDUCTION IN EXACERBATIONS
AND HOSPITALIZATIONS -
LUNG FUNCTION EFFICACY
(ACCORD I & II, ATTAIN) -
24-HOUR
CONTROL -
REDUCTION
IN RESCUE MED
tudorza significantly reduced copd exacerbations & associated hospitalizations2,*
Primary Endpoint: On-Treatment Reduction in Rate of Moderate or Severe COPD Exacerbations During 1st Year1,2,*
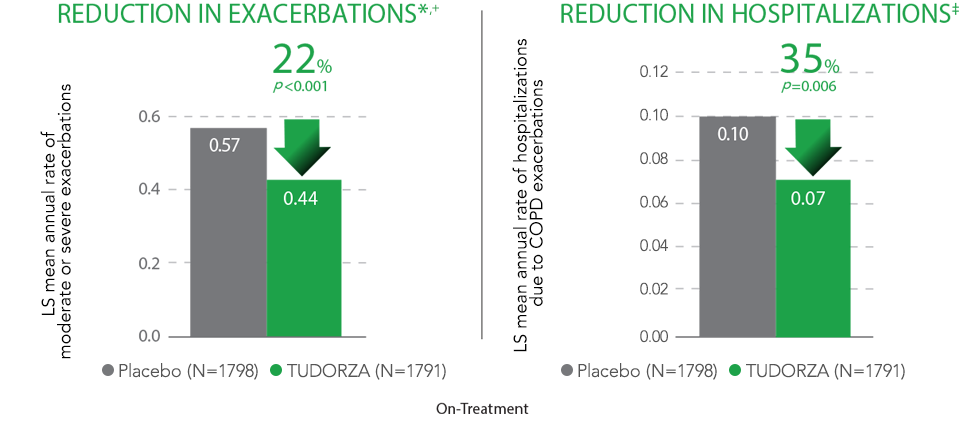
LS = Least Squares
- The key secondary endpoint in the study was on-study reductions in exacerbations of 17% and hospitalizations due to COPD by 28%
*Patients with stable, moderate-to-very severe COPD, and history of significant cardiovascular (CV) disease or cerebrovascular disease and/or significant risk factors.
†Exacerbation defined as increased COPD symptoms lasting greater than or equal to 2 days requiring treatment with either antibiotics and/or systemic corticosteroids or leading to hospitalizations or death.
‡Hospitalizations due to COPD exacerbations was a secondary endpoint.
DESCRIPTION OF ASCENT STUDY:
ASCENT-COPD was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, Phase IV study of up to 3
years in 3630 patients with moderate-to-very severe COPD. The study comprised a 2-week washout
period, followed by a double-blind treatment phase in which patients were randomized 1:1 to
aclidinium 400 mcg or placebo BID. The study enrolled patients with a clinical diagnosis of
moderate-to-very severe COPD who were >40 years, were current or former smokers with a smoking
history of >10 pack-years, had an FEV1
<80% predicted normal and a ratio of FEV1/FVC <0.7. Patients also had a history of
significant CV or cerebrovascular disease and/or significant risk factors.* The primary
efficacy endpoint was rate of moderate-to-very severe COPD exacerbations per patient per
year during the first year of treatment versus placebo. The primary safety endpoint was the
time to first major adverse CV event (MACE). The primary endpoints were met.
2
*Documented cerebrovascular disease (e.g., stroke or transient ischemic attack, carotid stenosis). Documented coronary artery disease (e.g., angioplasty/stent/bypass, angina, MI). Documented peripheral vascular disease or history of claudication. Two or more of the following CV risk factors as determined by the investigator: male >65 years or female >70 years, diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, waist circumference >40 inches for males and >38 inches for females, evidence of renal dysfunction (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate <60), and microalbuminuria (defined as>30-300 mcg/mg creatinine on a spot urine test or >30 mg creatinine on a 24-hour urine test; renal dysfunction criteria were added after the initiation of patient enrollment).
FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
FVC = forced vital capacity.
SUSTAINED IMPROVEMENT IN LUNG FUNCTION
Sustained improvement in lung function was demonstrated in two 12-week and one 24-week efficacy and safety COPD clinical studies.
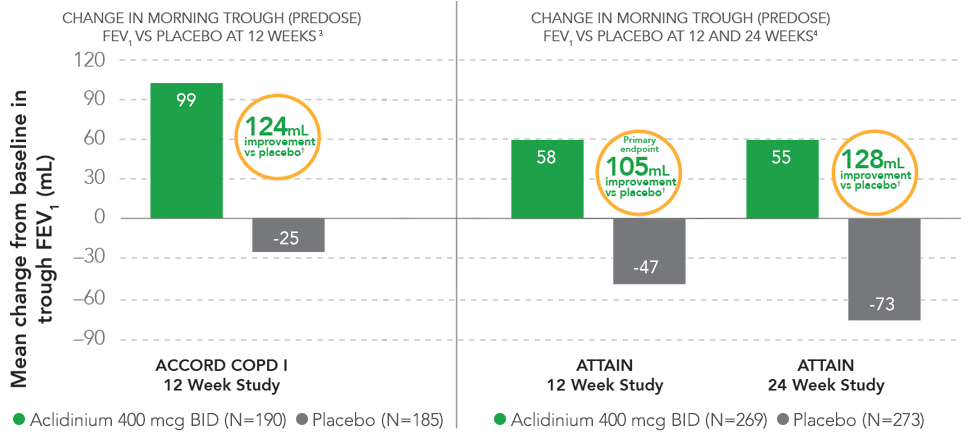
†P <0.0001 vs placebo.
- Statistically significant improvement in morning predose FEV1 was also
demonstrated in the ACCORD COPD II study5
— At 12 weeks, patients treated with TUDORZA 400 mcg achieved a 72-mL mean improvement in FEV1 over patients in the placebo group (P <0.001) - In ACCORD COPD I, the mean baseline FEV1 values were 1330 mL for the TUDORZA study group and 1380 mL for the placebo study group1,3; in ACCORD COPD II, the mean baseline FEV1 values were 1250 mL for the TUDORZA study group and 1460 mL for the placebo study group1,5
- In ATTAIN, the improvement in trough (predose) FEV1 was statistically significant; the difference vs placebo for trough (predose) FEV1 was 105 mL at 12 weeks and 128 mL at 24 weeks4
- Mean baseline FEV1 values in ATTAIN were 1510 mL for the TUDORZA study group and 1500 mL for the placebo study group1,4
DESCRIPTION OF ACCORD COPD I and ACCORD COPD II
STUDIES:
Two 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group
studies of 1105 patients with COPD compared aclidinium 400 mcg BID and aclidinium 200 mcg
BID to placebo BID. The studies enrolled patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD who
were aged ≥40 years, were current or former smokers with a smoking history of ≥10
pack-years, and had an FEV1 30% to <80% predicted normal and a ratio of FEV
1/FVC <0.7. The studies included a 2-week run-in period followed by a 12-week
treatment
period.1,3,5
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in morning trough (predose) FEV1 at 12 weeks.1,3,5
BID = twice daily.
FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
FVC = forced vital capacity.
DESCRIPTION OF ATTAIN STUDY:
A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study
of 828 patients with COPD compared aclidinium 400 mcg BID and aclidinium 200 mcg BID to
placebo BID. The study enrolled patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD who were aged
≥40 years, were current or former smokers with a smoking history of ≥10 pack-years, and
had an FEV1
<80% of predicted normal, and had a ratio of FEV1/FVC of <0.7. The study
included a 2-week run-in period followed by a 24-week treatment period.1,4
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in morning trough (predose) FEV1 at 12 weeks.1,4
TUDORZA IMPROVED LUNG FUNCTION IN THE MORNING AND EVENING1,6
In a Phase 2b crossover study with 7-day treatment periods:
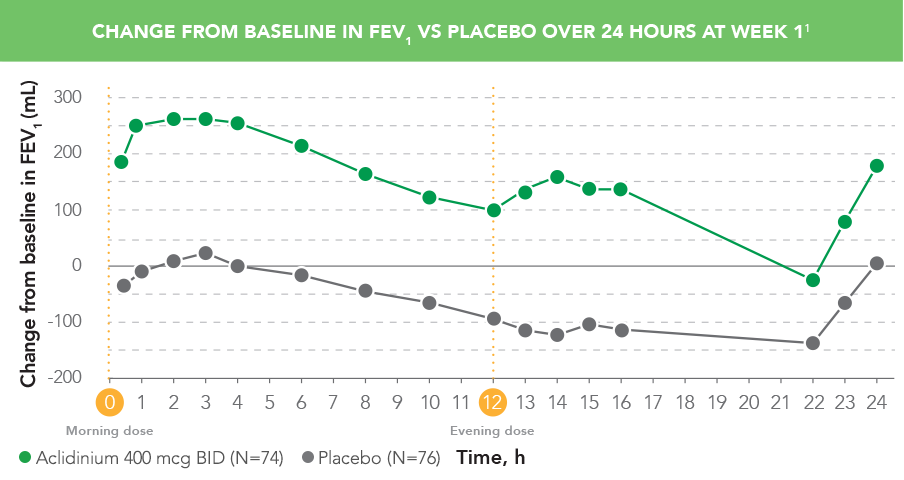
- TUDORZA provided patients with improved breathing in the evening with a second dose1,6
DESCRIPTION OF STUDY
A Phase 2b, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo- and active-controlled,
dose-ranging, crossover study assessed the efficacy and safety of TUDORZA in 79 patients with
moderate to severe COPD. The study included 7-day treatment periods (separated by 5-day
washout periods) with TUDORZA 400 mcg BID, 200 mcg BID (not approved), and 100 mcg BID (not
approved); formoterol active control; and placebo.
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in normalized FEV1 AUC0-12 post dose on Day 7. Change from baseline in FEV1 on Day 7 was an additional efficacy endpoint.1,6
FEV1= forced expiratory volume in 1 second; AUC = area under the curve.
TUDORZA SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCED
RESCUE MEDICATION USE1,3,4,7
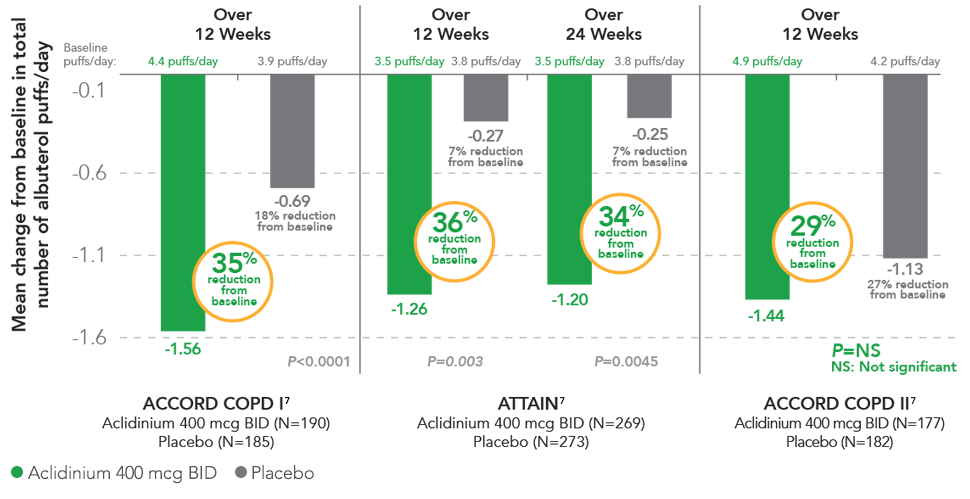
In 2 studies, TUDORZA provided significant reductions in daily rescue use compared to placebo over 12 weeks (ACCORD COPD I, ATTAIN) and 24 weeks (ATTAIN).1,3,4 In a third study (ACCORD COPD II), the reduction of daily rescue medication use for TUDORZA compared to placebo did not achieve statistical significance.1,5 In all 3 studies, the primary endpoint was the mean change from baseline in morning pre-dose (trough) FEV1 at 12 weeks.
DESCRIPTION OF ACCORD COPD I and ACCORD COPD II
STUDIES:
Two 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group
studies of 1105 patients with COPD compared aclidinium 400 mcg BID and aclidinium 200 mcg
BID to placebo BID. The studies enrolled patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD who
were aged ≥40 years, were current or former smokers with a smoking history of ≥10
pack-years, and had an FEV1 30% to <80% predicted normal and a ratio of FEV
1/FVC <0.7. The studies included a 2-week run-in period followed by a 12-week
treatment
period.1,3,5
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in morning trough (predose) FEV1 at 12 weeks.1,3,5
BID = twice daily.
FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
FVC = forced vital capacity.
DESCRIPTION OF ATTAIN STUDY:
A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study
of 828 patients with COPD compared aclidinium 400 mcg BID and aclidinium 200 mcg BID to
placebo BID. The study enrolled patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD who were aged
≥40 years, were current or former smokers with a smoking history of ≥10 pack-years, and
had an FEV1
<80% of predicted normal, and had a ratio of FEV1/FVC of <0.7. The study
included a 2-week run-in period followed by a 24-week treatment period.1,4
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in morning trough (predose) FEV1 at 12 weeks.1,4
 For US Healthcare Professionals
For US Healthcare Professionals